Stomach cancer usually does not give any symptoms in the early stages. However, the symptoms it causes are:
Weight loss
Abdominal pain (especially upper navel)
Difficulty swallowing
Loss of appetite or early satiety
Nausea
Fatigue or shortness of breath (usually due to anemia)
All these symptoms can be seen in diseases other than stomach cancer.
It is the most common test for stomach cancer. During this test, a thin tube with a camera is advanced from the mouth into the stomach. It is possible to view the esophagus, stomach and small intestine from the inside.
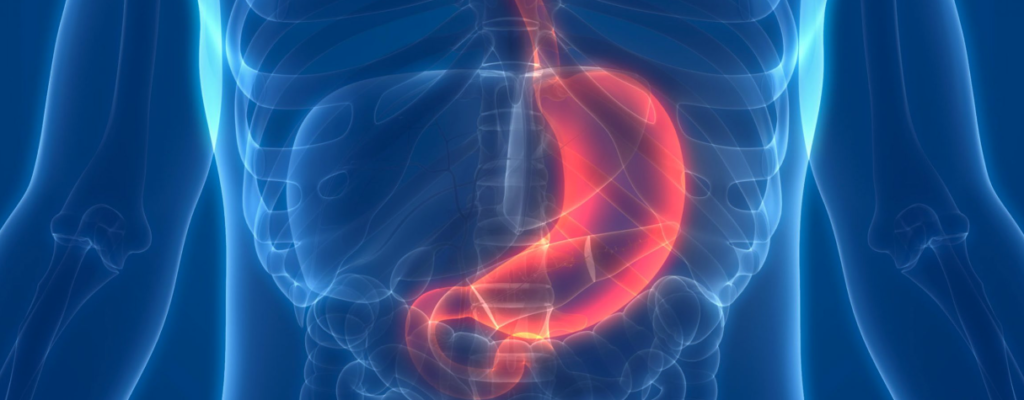
During endoscopy, a small sample of tissue is taken from an abnormal-looking area of the stomach and examined under a microscope.
Computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance (MR) etc. The tests create pictures of the inside of the body.
In addition, “Helicobacter pylori” infection should be checked with a stomach biopsy, breath test, blood test or other laboratory tests. This infection, which does not cause any problems most of the time, can cause conditions that can progress from open sores called “ulcers” in the stomach or duodenum to cancer in some people.
Typical risk factors for stomach cancer include genetic predisposition, gastric surgery, dietary factors, conditions that cause low stomach acid, and H. Pylori infection.

It is the most commonly used treatment method, and with this method, part or all of the stomach is removed together with the vessels feeding it and the accompanying fatty tissue and lymph nodes, depending on the location of the cancer. The continuity of the digestive system is ensured by connecting the small intestine with the remaining stomach tissue or esophagus.
Chemotherapy is the administration of drugs that kill cancer cells or stop their growth. Depending on the extent of spread of the disease at the time of diagnosis and the results of the pathological examination after surgery, chemotherapy can be applied before and/or after surgery.
It is the process of preventing the proliferation of cancer cells in a certain area with high-energy rays. It is generally applied in tumors of the upper part of the stomach.
It is the use of drugs that work with the body’s immune system to stop the development of cancer. It is applied in combination with chemotherapy.