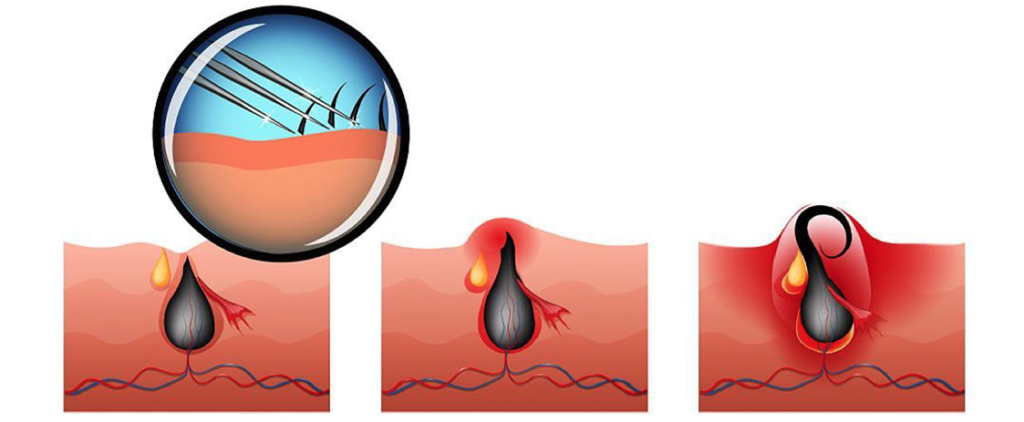
The current accepted theory about the formation of the disease; It is an acquired condition that occurs when the causes that damage or put pressure on the hair follicles in the coccyx cause the pores to open in the skin of this area, and the loose hairs and debris are collected in the opened pores. Recurrent infections of the pores lead to abscess and/or sinus formation and complaints.
It occurs most often in the late teens and early twenties, mostly in boys. It is less common in children and those older than 45 years.
Although the coccyx is the most common area, other parts of the body can also be affected, such as the navel and between the fingers.
Pilonidal disease, especially when infected, can be confused with some other conditions such as cellulitis and skin abscesses, hidradenitis suppurativa, anal abscesses.
Obesity
Regional trauma or irritation
Sedentary lifestyle or prolonged sitting
Deep cleft between hips
Increased hair density and lack of hygiene in this cleft area
Family history
The presence of one or more millimetric pores in the coccyx and accompanying swellings on the upper part of these pores and on the margins of the midline, which can be painful and runny (inflamed, bloody), enable the diagnosis to be made. No laboratory or imaging methods are required for diagnosis.
It can be detected without causing any complaints, or it can manifest itself with acute infection, abscess formation and many wounds with chronic discharge.
Patients who do not have any complaints or whose millimetric pores in the coccyx are discovered incidentally may not require treatment.
In case of abscess development, it must be surgically drained. After recovery, epilation of the area is required by applying hair removal products (spray, cream) or laser regularly. It is recommended not to shave the hairs with a razor.
In patients with chronic draining wounds, the most common method is surgical removal of the entire area containing the cysts. This procedure may be in the form of the removal of millimetric areas in the microsinusectomy method, as well as the removal of large tissues.
Then, the tissue space formed, the size of the wound, its location, recurrent disease state, etc. It is repaired with various closing methods depending on the factors. These methods are primary repair, Karydakis flap, Bascom procedure, Limberg flap, V-Y flap and other rotational flaps or wound healing with dressing by leaving it open.
Endoscopic pilonidal sinus treatment (Epsit) is a current method and is the removal of the diseased area by entering under the skin with a 3mm diameter camera.
Other methods applied as an alternative to surgical methods are injection of crystallized phenol, application of fibrin glue and use of negative pressure wound closure devices.